This flashcard is just one of a free flashcard set. See all flashcards!
95
What problems are addressed by the Extended Marching Cubes algorithm? How does it solve them?
Problems of Marching Cubes
Solution: Directed Distances
instead of an iso-value, store three directed distances for every vertex: exact distance to the surface crossing along every cube edge
Solution: Feature Detection / Sampling / Reconstruction
Feature Detection
based on the gradient values at the edge intersections, compute normal vectors:
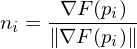
find the two normal vectors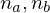 which span the largest angle
which span the largest angle
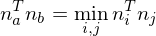
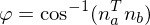
find the normal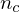 which forms the smallest angle to the orthogonal direction
which forms the smallest angle to the orthogonal direction 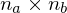
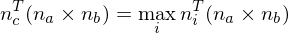
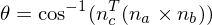
If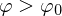 , we have detected a feature.
, we have detected a feature.
If additionally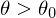 , the current feature is a corner feature (two large opening angles). Otherwise, it is an edge feature (one large opening angle).
, the current feature is a corner feature (two large opening angles). Otherwise, it is an edge feature (one large opening angle).
Feature Sampling
Find intersection point of tangent planes:
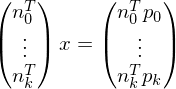
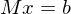
This might not have a unique solution:
Over-determined: No common intersection point. Find least-squares solution (closest to all planes).
Under-determined: Infinitely many intersection points. Find least-norm solution (closest to voxel center).
Solve using SVD:
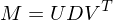
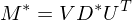
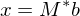
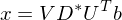
Feature Reconstruction
Look up cell configuration from Marching Cubes table. If in a feature cell, insert feature vertex at computed position and connect with a triangle fan. Flip edges so they align with feature edges.
- edge intersections are computed using linear interpolation (inaccurate)
- assumes smooth isosurface: sharp features within cells are lost (aliasing problem)
Solution: Directed Distances
instead of an iso-value, store three directed distances for every vertex: exact distance to the surface crossing along every cube edge
Solution: Feature Detection / Sampling / Reconstruction
Feature Detection
based on the gradient values at the edge intersections, compute normal vectors:
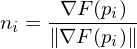
find the two normal vectors
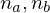 which span the largest angle
which span the largest angle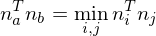
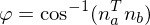
find the normal
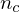 which forms the smallest angle to the orthogonal direction
which forms the smallest angle to the orthogonal direction 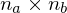
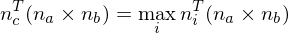
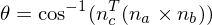
If
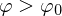 , we have detected a feature.
, we have detected a feature.If additionally
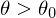 , the current feature is a corner feature (two large opening angles). Otherwise, it is an edge feature (one large opening angle).
, the current feature is a corner feature (two large opening angles). Otherwise, it is an edge feature (one large opening angle).Feature Sampling
Find intersection point of tangent planes:
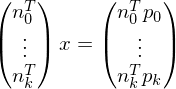
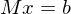
This might not have a unique solution:
Over-determined: No common intersection point. Find least-squares solution (closest to all planes).
Under-determined: Infinitely many intersection points. Find least-norm solution (closest to voxel center).
Solve using SVD:
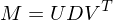
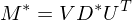
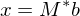
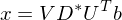
Feature Reconstruction
Look up cell configuration from Marching Cubes table. If in a feature cell, insert feature vertex at computed position and connect with a triangle fan. Flip edges so they align with feature edges.
Flashcard info:
Author: janisborn
Main topic: Informatik
Topic: Computergrafik
School / Univ.: RWTH Aachen
City: Aachen
Published: 18.05.2022

