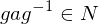Properties of Inverses
- If an element
 has both a left inverse
has both a left inverse 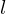 and a right inverse
and a right inverse 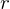 , i.e., if
, i.e., if 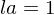 and
and 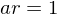 , then
, then 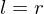 ,
,  is inveritble,
is inveritble, 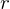 is its inverse
is its inverse - If
 is invertible, its inverse is unique
is invertible, its inverse is unique - Inverses multiply in the opposite order. If
 and
and 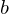 are invertible, so is the product
are invertible, so is the product 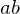 , and
, and 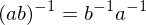 .
. - An element
 may have a left inverse or a right inverse, though it is not invertible.
may have a left inverse or a right inverse, though it is not invertible.
Group
A group 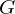 is a set with a law of composition which is
is a set with a law of composition which is
(1) associative
(2) has an identity element
(3) every element is invertible
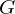 is a set with a law of composition which is
is a set with a law of composition which is(1) associative
(2) has an identity element
(3) every element is invertible
Cancellation Law
Let 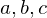 be elements of a group
be elements of a group 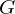 whose law of composition is written multiplicatively. If
whose law of composition is written multiplicatively. If 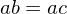 or if
or if 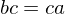 then
then 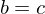 . If
. If 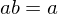 or if
or if 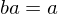 , then b = 1.
, then b = 1.
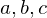 be elements of a group
be elements of a group 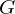 whose law of composition is written multiplicatively. If
whose law of composition is written multiplicatively. If 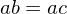 or if
or if 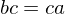 then
then 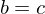 . If
. If 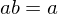 or if
or if 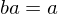 , then b = 1.
, then b = 1.Symmetric Group
The group of permutations of the set of indices 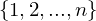 is called the symmetric group and is denoted by
is called the symmetric group and is denoted by 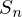 .
.
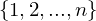 is called the symmetric group and is denoted by
is called the symmetric group and is denoted by 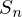 .
.Generators
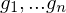 generate
generate 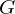 if every element in
if every element in 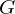 can be expressed as a combination of
can be expressed as a combination of 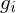 's and
's and 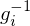 's using LoC.
's using LoC.Subgroups of 

Let  be a subgroup of the additive identity
be a subgroup of the additive identity 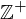 . Either
. Either  is the trivial subgroup
is the trivial subgroup 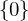 , or else it has the form:
, or else it has the form:
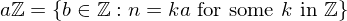
where is the smallest positive integer in
is the smallest positive integer in  .
.
 be a subgroup of the additive identity
be a subgroup of the additive identity 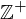 . Either
. Either  is the trivial subgroup
is the trivial subgroup 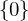 , or else it has the form:
, or else it has the form: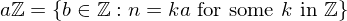
where
 is the smallest positive integer in
is the smallest positive integer in  .
.Division Algorithm
For any integer 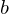 and positive integer
and positive integer  , there are integers
, there are integers 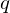 and
and 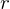 s.t.
s.t. 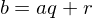 and
and 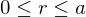
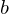 and positive integer
and positive integer  , there are integers
, there are integers 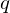 and
and 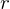 s.t.
s.t. 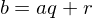 and
and 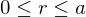
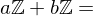 ?
?Let  and
and 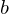 be integers, not both zero, and let
be integers, not both zero, and let 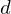 be their greatest common divisor, the positive integer that generates the subgroup
be their greatest common divisor, the positive integer that generates the subgroup 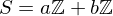 , i.e.
, i.e. 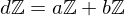 . Then
. Then
 and
and 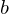 be integers, not both zero, and let
be integers, not both zero, and let 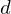 be their greatest common divisor, the positive integer that generates the subgroup
be their greatest common divisor, the positive integer that generates the subgroup 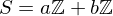 , i.e.
, i.e. 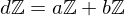 . Then
. Then-
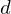 divides
divides  and
and 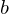 .
. - If an integer
 divides both
divides both  and
and 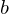 , it also divides
, it also divides 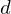
- There are integers
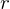 and
and  such that
such that 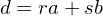
Fundamental Theorem of Arithmetic
If 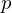 is a prime integer and divides
is a prime integer and divides 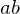 , then
, then 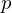 divides
divides  or
or 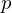 divides
divides 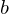 .
.
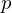 is a prime integer and divides
is a prime integer and divides 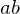 , then
, then 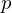 divides
divides  or
or 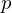 divides
divides 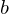 .
.Least Common Multiple
If 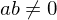 and
and 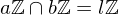 , where
, where 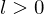 , then
, then 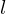 is the least common multiple of
is the least common multiple of 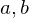 such that
such that
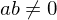 and
and 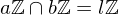 , where
, where 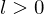 , then
, then 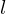 is the least common multiple of
is the least common multiple of 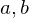 such that
such that-
 and
and 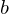 divide
divide 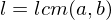
- If
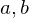 divide
divide 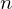 , then
, then 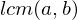 divide
divide 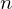
-
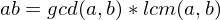
Properties of Cyclic Subgroups
Let 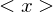 be the cyclic subgroup of
be the cyclic subgroup of 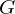 generated by
generated by 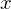 and let set
and let set 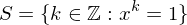 . Then
. Then
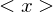 be the cyclic subgroup of
be the cyclic subgroup of 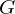 generated by
generated by 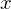 and let set
and let set 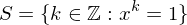 . Then
. Then -
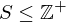
-
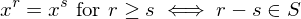
- Suppose
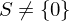 . Then
. Then 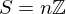 for some
for some 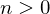 and
and 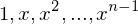 are distinct elements of
are distinct elements of 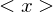 .
.
Homomorphisms
Let 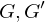 be two groups and
be two groups and 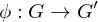 a map of the underlying sets. Then
a map of the underlying sets. Then 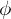 is a homomorphism if
is a homomorphism if
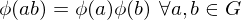
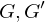 be two groups and
be two groups and 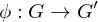 a map of the underlying sets. Then
a map of the underlying sets. Then 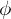 is a homomorphism if
is a homomorphism if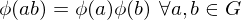
Properties of Group Homomorphisms
Let 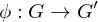 be a group homomorphism. Then
be a group homomorphism. Then
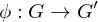 be a group homomorphism. Then
be a group homomorphism. Then- If
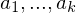 are elements of
are elements of 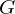 , then
, then 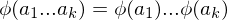
-
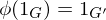
-
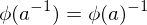
Composition of homomorphisms
If 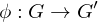 and
and 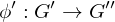 are group homomorphisms, then
are group homomorphisms, then
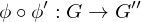 is a group homomorphism.
is a group homomorphism.
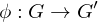 and
and 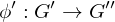 are group homomorphisms, then
are group homomorphisms, then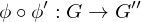 is a group homomorphism.
is a group homomorphism.Permutation Matricies
Let 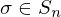 ,
,  be the standard basis vectors for
be the standard basis vectors for 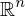 . Then the map from
. Then the map from 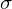 to its permutation matrix is a homomorphism defined as
to its permutation matrix is a homomorphism defined as
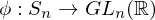

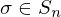 ,
,  be the standard basis vectors for
be the standard basis vectors for 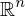 . Then the map from
. Then the map from 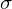 to its permutation matrix is a homomorphism defined as
to its permutation matrix is a homomorphism defined as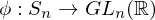

Sign Homomorphism
Let 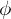 the permutation matrix homomorphism. Then
the permutation matrix homomorphism. Then 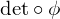 is the sign homomorphism.
is the sign homomorphism.
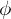 the permutation matrix homomorphism. Then
the permutation matrix homomorphism. Then 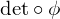 is the sign homomorphism.
is the sign homomorphism.- The image of the sign =
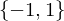
- The kernel of the sign is called the alternating group
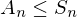
Property (2) of the Kernel
The kernel of a homomorphism is a normal subgroup
Also, every normal subgroup is the kernel of some homomorphism
Also, every normal subgroup is the kernel of some homomorphism
Inverse of Isomorphism
If 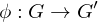 is an isomorphism, then the inverse map
is an isomorphism, then the inverse map 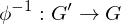 is also an isomorphism
is also an isomorphism
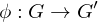 is an isomorphism, then the inverse map
is an isomorphism, then the inverse map 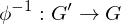 is also an isomorphism
is also an isomorphismPartition
A partition 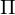 of a set
of a set  is a subdivision of
is a subdivision of  into nonoverlapping, nonempty subsets:
into nonoverlapping, nonempty subsets:
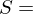 union of disjoint nonempty subsets
union of disjoint nonempty subsets
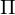 of a set
of a set  is a subdivision of
is a subdivision of  into nonoverlapping, nonempty subsets:
into nonoverlapping, nonempty subsets: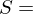 union of disjoint nonempty subsets
union of disjoint nonempty subsetsEquivalence Relation
A relation that holds between certain pairs of elements of  . We may write it as
. We may write it as 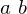 . An equivalence relation is required to be:
. An equivalence relation is required to be:
 . We may write it as
. We may write it as 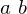 . An equivalence relation is required to be:
. An equivalence relation is required to be:- Transitive: If
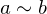 and
and 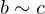 , then
, then 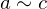
- Symmetric: If
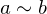 then
then 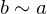
- Reflexive: For all
 ,
, 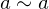
Equivalence Relation and Partition
An equivalence relation on a set  determines a partition of
determines a partition of  , and conversely.
, and conversely.
 determines a partition of
determines a partition of  , and conversely.
, and conversely.Equivalence Classes
Given an equivalence relation on a set  , the subsets of
, the subsets of  that are equivalence classes partition
that are equivalence classes partition 
 , the subsets of
, the subsets of  that are equivalence classes partition
that are equivalence classes partition 
Coset Partitions
The left Cosets of a subgroup  partition
partition 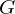 . Similarly for right Cosets
. Similarly for right Cosets
 partition
partition 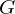 . Similarly for right Cosets
. Similarly for right CosetsKartensatzinfo:
Autor: CoboCards-User
Oberthema: Mathematics
Thema: Abstract Algebra
Schule / Uni: Rice University
Ort: Houston
Veröffentlicht: 12.02.2017
Tags: Ronan Mukamel
Schlagwörter Karten:
Alle Karten (46)
keine Schlagwörter



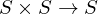
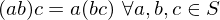
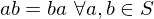
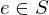
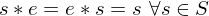
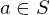 is invertivble if there is a
is invertivble if there is a 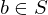 s.t.
s.t.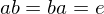
 ) denoted
) denoted 
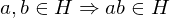 (closed under LOC)
(closed under LOC)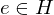 (identity)
(identity)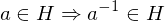 (inverses)
(inverses)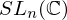
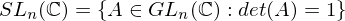
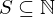 has a least element.
has a least element.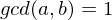
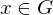 . The cyclic group generated by
. The cyclic group generated by 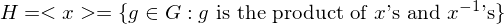
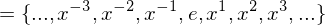
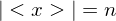 . Then
. Then 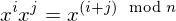 for
for 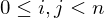
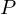 be a regular
be a regular 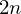 is
is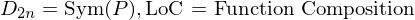
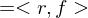
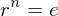
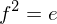
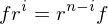
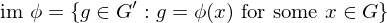
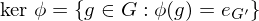
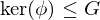 and
and 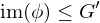
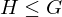 , a \in G. Then
, a \in G. Then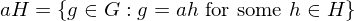
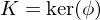 , and
, and 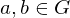 . TFAE:
. TFAE:
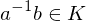
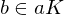
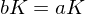
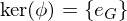
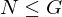 is called normal if
is called normal if  ,
,  implies
implies