Zu dieser Karteikarte gibt es einen kompletten Satz an Karteikarten. Kostenlos!
113
Explain the Bresenham / Midpoint algorithm for line drawing!
A line with integer-valued endpoints 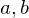 should be rasterized. W.l.o.g., we assume
should be rasterized. W.l.o.g., we assume 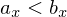 and
and 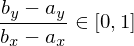 (we can rotate / flip our pixel grid to fulfill these conditions).
(we can rotate / flip our pixel grid to fulfill these conditions).
The line is rasterized by starting with a point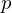 on the line at
on the line at  , and successively shifting
, and successively shifting 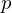 to the right
to the right
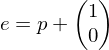 ,
,
or to the top right
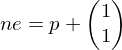 .
.
This decision is made based on whether the line passes above or below the midpoint
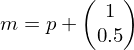
between and
and 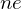 .
.
This condition can be checked by deriving an implicit representation of the line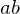 . By taking
. By taking 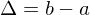 , we can define a normal to
, we can define a normal to 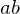 as
as
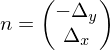
and thus derive the implicit representation
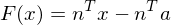 .
.
In order to decide whether to go East or Northeast, we introduce a decision variable, which is initially
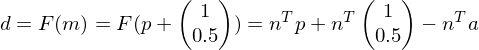 .
.
If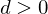 , we go East:
, we go East:
Update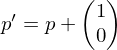 .
.
Update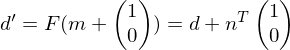 .
.
If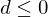 , we go Northeast:
, we go Northeast:
Update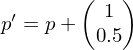 .
.
Update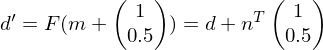 .
.
Values for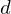 can be doubled, thus using only integer arithmetic.
can be doubled, thus using only integer arithmetic.
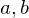 should be rasterized. W.l.o.g., we assume
should be rasterized. W.l.o.g., we assume 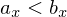 and
and 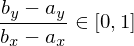 (we can rotate / flip our pixel grid to fulfill these conditions).
(we can rotate / flip our pixel grid to fulfill these conditions).The line is rasterized by starting with a point
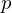 on the line at
on the line at  , and successively shifting
, and successively shifting 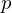 to the right
to the right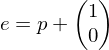 ,
,or to the top right
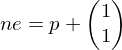 .
.This decision is made based on whether the line passes above or below the midpoint
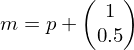
between
 and
and 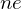 .
. This condition can be checked by deriving an implicit representation of the line
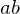 . By taking
. By taking 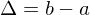 , we can define a normal to
, we can define a normal to 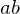 as
as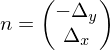
and thus derive the implicit representation
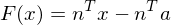 .
.In order to decide whether to go East or Northeast, we introduce a decision variable, which is initially
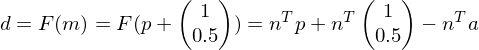 .
.If
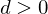 , we go East:
, we go East:Update
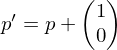 .
.Update
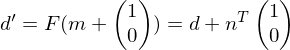 .
.If
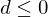 , we go Northeast:
, we go Northeast:Update
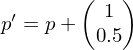 .
.Update
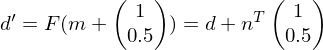 .
.Values for
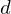 can be doubled, thus using only integer arithmetic.
can be doubled, thus using only integer arithmetic.Karteninfo:
Autor: janisborn
Oberthema: Informatik
Thema: Computergrafik
Schule / Uni: RWTH Aachen
Ort: Aachen
Veröffentlicht: 18.05.2022

