Zu dieser Karteikarte gibt es einen kompletten Satz an Karteikarten. Kostenlos!
14
How are Light Fields rendered? How can we do this on the GPU?
First, consider bi-linear interpolation. In order to determine the color at a position 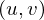 lying between four grid samples. Each grid sample at a position
lying between four grid samples. Each grid sample at a position 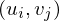 has an influence of
has an influence of
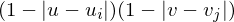
on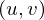 .
.
Given: Light Field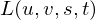
Let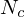 be the coordinates of the four pixels around
be the coordinates of the four pixels around 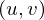 on the camera plane and
on the camera plane and 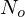 the coordinates of the four pixels around
the coordinates of the four pixels around 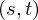 on the object plane.
on the object plane.
For each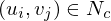 , we compute an interpolated color value
, we compute an interpolated color value 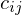 from the four neighboring samples
from the four neighboring samples 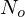 on the object plane based on the position
on the object plane based on the position 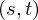 .
.
Then, we compute a interpolated color value from the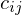 , based on the position
, based on the position 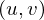 .
.
Since we do a linear interpolation twice, this is called quad-linear interpolation.
GPU Implementation
Obtaining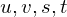 coordinates for every pixel
coordinates for every pixel
Draw two quads: One for the object plane, one for the camera plane. As a texture, use a smooth color gradient from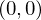 lower left to
lower left to 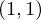 upper right. The rasterized colors are the
upper right. The rasterized colors are the 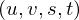 coordinates for every pixel.
coordinates for every pixel.
Bi-Linear Interpolation on the Object Plane
We get this for free through texture interpolation: For each camera plane pixel, render one quad. As texture coordinates for the quad, use the respective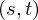 coordinates at that position.
coordinates at that position.
Quad-Linear Interpolation
Instead of rendering one quad per camera plane pixel, render four quads surrounding the pixel with alpha blending and fade out the contribution towards the outer edges.
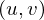 lying between four grid samples. Each grid sample at a position
lying between four grid samples. Each grid sample at a position 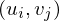 has an influence of
has an influence of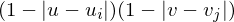
on
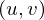 .
.Given: Light Field
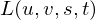
Let
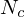 be the coordinates of the four pixels around
be the coordinates of the four pixels around 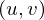 on the camera plane and
on the camera plane and  the coordinates of the four pixels around
the coordinates of the four pixels around 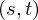 on the object plane.
on the object plane.For each
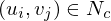 , we compute an interpolated color value
, we compute an interpolated color value 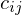 from the four neighboring samples
from the four neighboring samples 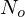 on the object plane based on the position
on the object plane based on the position 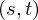 .
.Then, we compute a interpolated color value from the
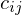 , based on the position
, based on the position 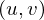 .
.Since we do a linear interpolation twice, this is called quad-linear interpolation.
GPU Implementation
Obtaining
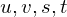 coordinates for every pixel
coordinates for every pixelDraw two quads: One for the object plane, one for the camera plane. As a texture, use a smooth color gradient from
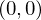 lower left to
lower left to 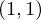 upper right. The rasterized colors are the
upper right. The rasterized colors are the 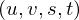 coordinates for every pixel.
coordinates for every pixel.Bi-Linear Interpolation on the Object Plane
We get this for free through texture interpolation: For each camera plane pixel, render one quad. As texture coordinates for the quad, use the respective
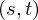 coordinates at that position.
coordinates at that position.Quad-Linear Interpolation
Instead of rendering one quad per camera plane pixel, render four quads surrounding the pixel with alpha blending and fade out the contribution towards the outer edges.
Karteninfo:
Autor: janisborn
Oberthema: Informatik
Thema: Computergrafik
Schule / Uni: RWTH Aachen
Ort: Aachen
Veröffentlicht: 18.05.2022

