Actinomycetes: Morphology/Characterization & Products
Gram-Positive bacteria
Grows as filaments and forms spores when nutrients run out
Produce Antibiotics:
Tetracyclines
Macrolides (erythromycin)
Aminoglycosides (Streptomycin, Gentamycin)
Grows as filaments and forms spores when nutrients run out
Produce Antibiotics:
Tetracyclines
Macrolides (erythromycin)
Aminoglycosides (Streptomycin, Gentamycin)
Nocardiaa spp
What kind of organism? How is it transmitted? What kinds of Infections can it cause?
What kind of organism? How is it transmitted? What kinds of Infections can it cause?
Opportunistic Pathogen
Transmitted via inhalation (lungs) or trauma (cutaneous infection)
Can cause
Pulmonary disease (bronchitis, pneumoniae, lung abscesses)
Cutaneous Infections ( Lymphocutaneous infection, cellulitis, subcutanous abscesses)
Secondary CNS infections (Meningitis, Brain Abcesses)
Transmitted via inhalation (lungs) or trauma (cutaneous infection)
Can cause
Pulmonary disease (bronchitis, pneumoniae, lung abscesses)
Cutaneous Infections ( Lymphocutaneous infection, cellulitis, subcutanous abscesses)
Secondary CNS infections (Meningitis, Brain Abcesses)
Actinomycetes: Nocardia spp.
Characterization?
Characterization?
Strict aerobe
Partial acid-fast stain
Catalase positive
Some cording
Partial acid-fast stain
Catalase positive
Some cording
What is Whipple's Disease? What class of organisms causes it? What is the primary problem, and what are the associated symptoms? Epidemiology
Caused by Actinomycetes
Causes lesions on the small intestine. Damages the villi => Poor nutrition
Associated Symptoms:
Look like fasting, weight loss
Men (80%) during middle age
higher in Caucasians (possibly genetic)
Causes lesions on the small intestine. Damages the villi => Poor nutrition
Associated Symptoms:
Look like fasting, weight loss
Men (80%) during middle age
higher in Caucasians (possibly genetic)
What group of organism does the Streptomyces family belong to? What is their morphology? Why are they medically significant
Actinomycetes
Forms hyphae-> Spores as nutrients depleted, otherwise filamentous network in soil
Produces streptomycin
Forms hyphae-> Spores as nutrients depleted, otherwise filamentous network in soil
Produces streptomycin
Mycobacterium:
What are the 2 major diseases that are caused by Mycobacterium
What are the 2 major diseases that are caused by Mycobacterium
Leprosy and Tuberculosis
How is Mycobacterium Avium transmitted? What are its structural characteristics? Where does it grow?
IIntracellular organism
Weakly Gram positive, acid fast
Lipid-rich cell wall.
Transmitted via food / water.
prevalent in Immunocompromised patients (mostly in this group)
Generates chronic pulmonary disease (middle lobe infiltrates / solitary nodules). Can also progress to disseminated disease
Weakly Gram positive, acid fast
Lipid-rich cell wall.
Transmitted via food / water.
prevalent in Immunocompromised patients (mostly in this group)
Generates chronic pulmonary disease (middle lobe infiltrates / solitary nodules). Can also progress to disseminated disease
Mycobacterium Leprae
What are the 4 forms of Leprosy?
How is it transmitted?
What are the problems that it causes?
Where does it grow?
How is it diagnosed?
What are the 4 forms of Leprosy?
How is it transmitted?
What are the problems that it causes?
Where does it grow?
How is it diagnosed?
Intracellular growth - hard to culture on artificial media
Tuberculoid Leprosy
Borderline tuberculoid leprosy
Borderline Lepromatous leprosy
Lepromatous leprosy
All caused by M. leprae
transmitted by contact, aerosols, inhalation
Grows intracellularly
Causes skin lesions (can fuse fingers together). Damage to nerves
Diagnosed with skin test (lepromin). Or can use Light Microscopy with AFB stain
Tuberculoid Leprosy
Borderline tuberculoid leprosy
Borderline Lepromatous leprosy
Lepromatous leprosy
All caused by M. leprae
transmitted by contact, aerosols, inhalation
Grows intracellularly
Causes skin lesions (can fuse fingers together). Damage to nerves
Diagnosed with skin test (lepromin). Or can use Light Microscopy with AFB stain
What are the 3 kinds of bugs in the M. Tuberculosis complex?
M. tuberculosis
M. Bovis - a modified form of this is used to make BCG
M. Africanum
M. Bovis is no longer found in the US, but can still find it if a person immigrates
Diagnose using 3 early morning sputum samples
M. Bovis - a modified form of this is used to make BCG
M. Africanum
M. Bovis is no longer found in the US, but can still find it if a person immigrates
Diagnose using 3 early morning sputum samples
When is BCG administerd? What is the lifespan of the protection?
BCG only protects against TB early in life, not later in life
How many new cases of TB are there per year? What country has the most new cases per year? What country has the highest rate?
9M new cases
2M deaths
China has a lot of new cases
Africa has a very high incidence rate
2M deaths
China has a lot of new cases
Africa has a very high incidence rate
How does a person get an active infection?
2 ways:
1) Early transmission as kid. Latency. Reactivated disease when older / immunocompromised (1/3 of cases like this)
2) Recent transmission
1) Early transmission as kid. Latency. Reactivated disease when older / immunocompromised (1/3 of cases like this)
2) Recent transmission
What is the immune response to TB that can be evident on XR? What can go wrong?
immune system responds:
TGF-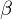 , IFN-
, IFN-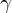 , IL-12
, IL-12
Granuloma formed around the disease to wall it off. These can be seen on XR
If the granuloma breaks, then you can get persistence of the disease
TGF-
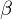 , IFN-
, IFN-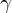 , IL-12
, IL-12Granuloma formed around the disease to wall it off. These can be seen on XR
If the granuloma breaks, then you can get persistence of the disease
Why do we care about Mycobacterial Cell Wall?
Inhibits drug entry
has Glycolipid surface molecules associated with MYCOLIC ACIDS
has Glycolipid surface molecules associated with MYCOLIC ACIDS
Slow growing mycobacteria vs. fast-growing mycobacteria
Are the ones we care about slow or fast growing? Which ones are they?
Are the ones we care about slow or fast growing? Which ones are they?
Slow growing:
M. tuberculosis, M. Avium complex, M. Kansasii
The ones we care about are slow growing
Fast Growing:
M. Chelonae, M. Fortuitm, M. Abscess
M. tuberculosis, M. Avium complex, M. Kansasii
The ones we care about are slow growing
Fast Growing:
M. Chelonae, M. Fortuitm, M. Abscess
Symptoms of TB
1) Chronic cough (>= 15 days)
2) Night Sweats
3) Fever
4) Weight Loss
5) Hemoptysis
6) Fatigue, Shortness of breath
2) Night Sweats
3) Fever
4) Weight Loss
5) Hemoptysis
6) Fatigue, Shortness of breath
What are the tools used for diagnosis?
Stethescope
CXR
AFB (Acid Fast Bacilli) stain and LM can be used to diagnose. But this requires training, and even in the best cases can be non-specific.
- This also requires cultures, which in the US require stringent safety methods
Tuberculin Skin Testing - test for LATENT infection. threshold depends on the pt. If HIV / immunesupressed, threshold is lower.
Quantiferon-Gold. Use IELISA to see how much IFN-##\gamma#
ELISPOT-TB. newset one
CXR
AFB (Acid Fast Bacilli) stain and LM can be used to diagnose. But this requires training, and even in the best cases can be non-specific.
- This also requires cultures, which in the US require stringent safety methods
Tuberculin Skin Testing - test for LATENT infection. threshold depends on the pt. If HIV / immunesupressed, threshold is lower.
Quantiferon-Gold. Use IELISA to see how much IFN-##\gamma#
ELISPOT-TB. newset one
What's special about CA & TB?
CA has a lot of migrants, which means that it has a much higher incidence rate.
Estimate about 3M latent infections in the country (10%)
If PPD positive, treat with 9mo course of Isoniazide
If active TB, then you use multiple drugs for 6 months.
Estimate about 3M latent infections in the country (10%)
If PPD positive, treat with 9mo course of Isoniazide
If active TB, then you use multiple drugs for 6 months.
Kartensatzinfo:
Autor: yaoyu
Oberthema: Biology
Thema: Microbiology
Veröffentlicht: 11.02.2010
Tags: Respiratory Infections
Schlagwörter Karten:
Alle Karten (19)
keine Schlagwörter



