name the five typcial features of a vertebra.
1. vertebral body
2. vertebral arch , forming a roof over the vertebral foramen.
a. pedicle
b. lamina
3. superior and inferior vertebral notch on each pedicle forms an interverebtral foramen with the adjacent vertebra for passage of spinal nerves and associated vessels.
4. paired superior and inferior articular processes
5. spinous and transverse processes for attachment of muscles and ligaments
a. transverse processes
2. vertebral arch , forming a roof over the vertebral foramen.
a. pedicle
b. lamina
3. superior and inferior vertebral notch on each pedicle forms an interverebtral foramen with the adjacent vertebra for passage of spinal nerves and associated vessels.
4. paired superior and inferior articular processes
5. spinous and transverse processes for attachment of muscles and ligaments
a. transverse processes
the superfical extrinsic back muscles can be kind of subdivided into a more superfical and a more deep group although both still belong to the sup. extr. muscles. name them
more superficial: latissiumus dorsi and trapezius
more deep: levator scapulae, rhomboid major and minor
in total five
more deep: levator scapulae, rhomboid major and minor
in total five
by what nerves and arteries is the intermediate layer of the extrinsic muscles supplied?
intercostal nerves and arteries

1) pedicle
2) transverse process
3) lamina
4) spinous process
5)vertebral arch
6)-
7)vertebral body
2) transverse process
3) lamina
4) spinous process
5)vertebral arch
6)-
7)vertebral body

1) superior vertebral notch
2) pedicle
3)vertebral body
4)inferior vertebral notch
5)inferior articular provess
6) lamina
7) spinous process
8)transverse process
9)superior articular process
2) pedicle
3)vertebral body
4)inferior vertebral notch
5)inferior articular provess
6) lamina
7) spinous process
8)transverse process
9)superior articular process
the intrinsic back muscles have 4 things in common, name them
1) move the spinal column
2) fill in the hollow between the spninous and transverse process, in the thorax they fill in the angles of the rib, some extend into the back of neck
3) are in tube of fascia, in neck called prevertebral fascia, below neck thoracolumbar fascia
inferior part of tube fused with tendon of superficial back muscles to form lumbar aponeurosis
4)innervated by dorsal rami of spinal nerves
2) fill in the hollow between the spninous and transverse process, in the thorax they fill in the angles of the rib, some extend into the back of neck
3) are in tube of fascia, in neck called prevertebral fascia, below neck thoracolumbar fascia
inferior part of tube fused with tendon of superficial back muscles to form lumbar aponeurosis
4)innervated by dorsal rami of spinal nerves
the superficial back muscles can be subdivided itno three furhter groups. name them
superfical spinotransversalis musles ( slenius cervicis and splenius capitis)
itnermediate erector spinae
deep transversospinales
itnermediate erector spinae
deep transversospinales
there are the muscles of the superficial intrinsic back muscles. name them


ligamentum nuchae
2 splenius capitis (attaches to the occipital bone and mastoid process)
3 splenius cervicis (attaces to the transverse process of the upper cerical vertebraue)
both run form the cervical and thoracic spinous processes and ligamentum nuchae
action: bilaterally draw head backwards (extending the neck), unilaterally rotate nekc to ipsilateral side
2 splenius capitis (attaches to the occipital bone and mastoid process)
3 splenius cervicis (attaces to the transverse process of the upper cerical vertebraue)
both run form the cervical and thoracic spinous processes and ligamentum nuchae
action: bilaterally draw head backwards (extending the neck), unilaterally rotate nekc to ipsilateral side
there are the muscles of the intermediate layer of the intrinsic musles which are also called the erector spinae.
name them.

name them.

1 spinalis capitis
2 longissimus captis
3 spinalis cervicis
4 longissimus cervicis
5 iliocostalis cervicis
6 spinalis thoracis
7 longissimus thoracis
8 iliocostalis thoracis
9 iliocostalis lumborum
2 longissimus captis
3 spinalis cervicis
4 longissimus cervicis
5 iliocostalis cervicis
6 spinalis thoracis
7 longissimus thoracis
8 iliocostalis thoracis
9 iliocostalis lumborum
this picture depicts the deep intrinsic muscles of the back. name them. they are collectivley cale dthe transversospinales.


1 semispinalis captitis
2 semispinalis thoracis
3 rotatores thoracis (short and long)
4 levatores costarum (short and long)
5 multifidus
6 intertransversarius
2 semispinalis thoracis
3 rotatores thoracis (short and long)
4 levatores costarum (short and long)
5 multifidus
6 intertransversarius
what part do the deep intrisnic muscles of the back occupy?
the space betwen the transverse process andt eh spinous process of the vertebrae
which one of the deep intrisnic muscles of the back is the most superficial one? where does it arise? where does it attach to?
semispinalis
starts at lower thoracic regions, attaches to occipital part of the skull
starts at lower thoracic regions, attaches to occipital part of the skull
whcih muscle do we find below the semispinalis?
mulitifidus ( more promindent in the lumbar region)
whcih muscle is the deepest of the depp intrinsic muscle of the back?
rotatores ( present thoughout the colunn, best prominent in thoracic region)
what is the action of the transversospinales muscle?
extension of the vertebral column
unilateral contraciton: pulls spinous processes towards transverse process causing rotation towards the opposite side
bilateral contraciton contraction fo semispinalis capitis: pulls head posteriorly , unilateral contraciton puuls htead posteriorly and rotates to opposite side
unilateral contraciton: pulls spinous processes towards transverse process causing rotation towards the opposite side
bilateral contraciton contraction fo semispinalis capitis: pulls head posteriorly , unilateral contraciton puuls htead posteriorly and rotates to opposite side
what type of muscle is the levatores costarum?
arise from the transverse processes of c7 to t 11 and attach to the rib inserting near the tubercle
is a segmental muslce of the back (their contraction elevates the rib)
occurs deep in the back
is a segmental muslce of the back (their contraction elevates the rib)
occurs deep in the back
what are the interspinales and intertransversarii?
true segmental muscles of back
span between adjacent spinous processes (interspinales) and between adjacent transverse proceses (intertransversarii)
postural muscles stailising adjacent vertebraes thus allowing action fo the larger muscles
span between adjacent spinous processes (interspinales) and between adjacent transverse proceses (intertransversarii)
postural muscles stailising adjacent vertebraes thus allowing action fo the larger muscles
what muscles cause flexion of the lumbar and thoracic joints?
bilateral action of: rectus abdominis
psoas major
gravity
lateral flexion: unilateral action of: iliocostalis thoracis and lumborum,
longissimus thoracis
multifidus
internal and external oblique
quadratus lumborum
rhomboids
serratur anterior
psoas major
gravity
lateral flexion: unilateral action of: iliocostalis thoracis and lumborum,
longissimus thoracis
multifidus
internal and external oblique
quadratus lumborum
rhomboids
serratur anterior
what muscles cause rotation of the lumbar and thoracic joints?
unilateral action of
rotatores
multifidus
iliocostalis
longissimus
external oblique and contralateral internal obliuqe
spelius thoracis
rotatores
multifidus
iliocostalis
longissimus
external oblique and contralateral internal obliuqe
spelius thoracis
what muscles cause extension of the lumbar and thoracic joints?
bilateral action of:
erector spinae
multifidus
semispinalis thoracis
erector spinae
multifidus
semispinalis thoracis
name the blood supply of the spinal cord
one anterior (comes fromt eh vertebral arteries which in turn cme form the subclavian artery) and two posterior (also vertebral artery) spinal arteries
list the blood supply of the vertebral column
Vertebrae receive their blood supply segmentally from branches of deeply situated arteries in neck,
thorax, abdomen and pelvis.
thorax, abdomen and pelvis.
explain the venous drainage of the spinal cord and the vertebral column
-Drainage of the vertebral column:
-via the vertebral venous plexuses. The internal vertebral venous plexus runs the length of the entire vertebral canal; it receives venous blood from the spinal cord and the vertebral bodies. The vertebral body of each vertebra contains erythropoietic bone marrow;
newly formed red blood cells are transported from each vertebral body into the circulation via two basivertebral veins from each vertebra.
All of the veins in the internal vertebral venous plexus are valveless. Veins from the internal vertebral venous plexus pass through each intervertebral foramen to drain into the external vertebral venous
- external venous plexus drains into larger veins of thorax, abdomen and neck
-via the vertebral venous plexuses. The internal vertebral venous plexus runs the length of the entire vertebral canal; it receives venous blood from the spinal cord and the vertebral bodies. The vertebral body of each vertebra contains erythropoietic bone marrow;
newly formed red blood cells are transported from each vertebral body into the circulation via two basivertebral veins from each vertebra.
All of the veins in the internal vertebral venous plexus are valveless. Veins from the internal vertebral venous plexus pass through each intervertebral foramen to drain into the external vertebral venous
- external venous plexus drains into larger veins of thorax, abdomen and neck
what is a disc herniation? cause by what? and causes what?
caused by acute back sprain hwcih ruptures the nucleus polposus though the annulus fibrosis
extrudes through the intervertebral foramen and thereby compressing teh spinal nerve causing pain
long term compression can end up in anastehsia and muscle weakness pr prarlysis of the region supplied by the nerve
mostly affects discs at the felxibel aprts (lower cervial and lumabr discs mostly affected)
herniation of disc between 1 and s 1 results in pressure on s1 , produced pain is called sciatica as it ivolves the sciatic nerve, pain is felt down the back of the thigh, leg and latearl side of the food

extrudes through the intervertebral foramen and thereby compressing teh spinal nerve causing pain
long term compression can end up in anastehsia and muscle weakness pr prarlysis of the region supplied by the nerve
mostly affects discs at the felxibel aprts (lower cervial and lumabr discs mostly affected)
herniation of disc between 1 and s 1 results in pressure on s1 , produced pain is called sciatica as it ivolves the sciatic nerve, pain is felt down the back of the thigh, leg and latearl side of the food

the musles of the back can be divided into two main groups. name them
extrinsic musles (superficial and intermediate)
intrinisc muscles ( superficial , intermeidate, deep including the erector spinae proper)
intrinisc muscles ( superficial , intermeidate, deep including the erector spinae proper)

this is a pic of the superficial extrinsic muslces. identify them.
1 levator scapuale
2 trapezius
3 rhomboid minor
4 rhomboid major
5 lattisimus dorso
2 trapezius
3 rhomboid minor
4 rhomboid major
5 lattisimus dorso

there are the muscles of the intermediate layer of the extrinisic musles, identiy them
1 serratur posterior superior
2 posteror layer of thoracolumbar fasica
3 serratour posterior inferior
2 posteror layer of thoracolumbar fasica
3 serratour posterior inferior
the intrinsic musles can be divided into superficial intermediate and deep, name the names of them
1. Superficial ‘spinotransversales’ muscles (splenius cervicis and splenius capitis)
2. Intermediate ‘erector spinae’ group of muscles
3. Deep ‘transversospinales’ muscle
2. Intermediate ‘erector spinae’ group of muscles
3. Deep ‘transversospinales’ muscle
spinotransversales are two muscles and belong to the superficial intrinsic back muscles, name them and their attachment and action
splenius capitis
to occipital bone and mastoid process from Lower half of ligamentum nuchae; spinous processes of vertebrae CVII to TIV
splenius cervicis
spinous processes of the 3 to the 6 thoracic vertebrae to posterior tubercles of the transverse processes of the upper two or three cervical vertebrae.
draws head backwads (extending) and rotate head
to occipital bone and mastoid process from Lower half of ligamentum nuchae; spinous processes of vertebrae CVII to TIV
splenius cervicis
spinous processes of the 3 to the 6 thoracic vertebrae to posterior tubercles of the transverse processes of the upper two or three cervical vertebrae.
draws head backwads (extending) and rotate head
the erector spinae muscles divide into three mucsles, name them medially to llaterally
spinalis capitis, thoracis, cervicis
longissimus cervicis captitis, cervicis, thoracis, lumborum
iliocostalis cervicis cervicis, throcacis
longissimus cervicis captitis, cervicis, thoracis, lumborum
iliocostalis cervicis cervicis, throcacis
what are the actions of the erector spinae muscles? (three)
extend
extrinsically contract to flex column
flex column laterallz or turn head ipsilaterally
extrinsically contract to flex column
flex column laterallz or turn head ipsilaterally
name the 6 deep intrinsic muscles of the back
semispinalis sapitis, thoracis
multifidus
intertransversarius
levator costarum
rotatores thoracis
interspinales
multifidus
intertransversarius
levator costarum
rotatores thoracis
interspinales
what are the three segmental back muscles?
levatores costarum
interspinales
intertransversii
interspinales
intertransversii
through what feature does the vertebral artery pass through?
foramen transversarium (absend sometimes at c7)

a foramen tranversarium
b vertebral body
c intrasverse process
d spinours process
e vertebral canal
b vertebral body
c intrasverse process
d spinours process
e vertebral canal
name 5 peculiarities of the atlas c1
1has no spinous process
2no body
3facets for occipital condyle
4anterior and posterior arch, have tubercles
5medial tubercle for attachment of transverse ligament (holds dens in place)
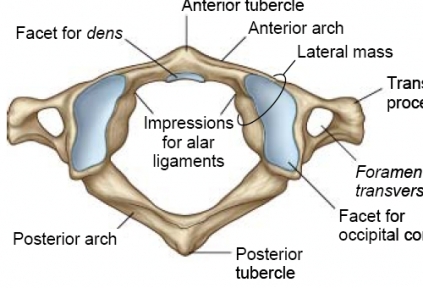
2no body
3facets for occipital condyle
4anterior and posterior arch, have tubercles
5medial tubercle for attachment of transverse ligament (holds dens in place)

name three pecularities of the axis c2 (atlas rotates on it (no movement, whereas yes movement occurs between skull and atlas)
flat surfaces superior articular facets (atlas articulates on it)
dens (odontoid process held in place by the transverse ligament of the atlas
large bifid spinous process ( can be felt in the nuchal furrow)

dens (odontoid process held in place by the transverse ligament of the atlas
large bifid spinous process ( can be felt in the nuchal furrow)

vertebrae are held together by amongst other things a facet joint. name the type of it
say what other things there are to hold the vertebrae together
say what other things there are to hold the vertebrae together
zygapophyseal joint (connect the articuar processes of adjacent vertebraes)
intervertebral discs, ligaments
intervertebral discs, ligaments
intervertebral discs help to hold the vertebraes together. they are composed of two different structures, name them.
annulus fibrosus (outer fibrocartilage ring)
nucleus pulposus (gelationous interior)
nucleus pulposus (gelationous interior)
there are three ligaments holding the vertebrae together. Name them.
anterior and posterior longitudional ligaments (bands anterior and posterior to the vertebral bodies)
ligamenta flava (elastic, unite laminae within the vertebral canal and provide elastic recoil to straighten the flexed back)
supraspinour and itnerspinous ligament (connect vertebral spines)

ligamenta flava (elastic, unite laminae within the vertebral canal and provide elastic recoil to straighten the flexed back)
supraspinour and itnerspinous ligament (connect vertebral spines)

what is the nuchal ligament?
extenson of supraspinous ligament
It extends from the external occipital protuberance and median nuchal line to the spinous process of the seventh cervical vertebra.
It extends from the external occipital protuberance and median nuchal line to the spinous process of the seventh cervical vertebra.
Kartensatzinfo:
Autor: Schnuschnax
Oberthema: Medicine
Thema: Anatomy
Veröffentlicht: 09.02.2010
Schlagwörter Karten:
Alle Karten (51)
keine Schlagwörter









