This flashcard is just one of a free flashcard set. See all flashcards!
6
How can we classify surface curvature in the continuous case? What is a discrete approximation for triangle meshes?
If we have a parametric surface 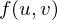 , we can take its taylor expansion
, we can take its taylor expansion
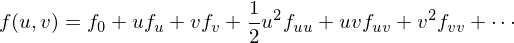
We can now reparametrize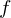 such that
such that 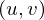 lies in the origin and the plane
lies in the origin and the plane 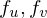 is parallel to
is parallel to 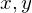
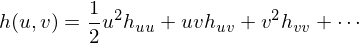
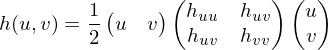
Since this matrix is symmetric and real-valued, we can do an eigendecomposition:
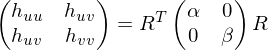
From the eigenvalues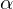 and
and 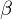 , we can derive two characteristics for local curvature:
, we can derive two characteristics for local curvature:
Mean Curvature: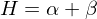
Gaussian Curvature: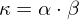
Which has the following interpretations:
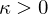 : Cap / Peak / Valley (elliptic)
: Cap / Peak / Valley (elliptic)
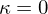 : Cylinder (parabolic)
: Cylinder (parabolic)
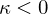 : Saddle (hyperbolic)
: Saddle (hyperbolic)
The eigenvectors corresponding to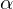 and
and 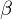 represent the respective curvature directions and are orthogonal.
represent the respective curvature directions and are orthogonal.
Shape Operator
Approximates curvature for triangle meshes.
For each edge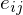 : atomic shape operator
: atomic shape operator
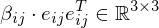
where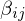 is the angle between the triangle normals
is the angle between the triangle normals 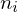
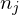 .
.
Around a vertex, we compute the atomic shape operators of all edges in the vicinity
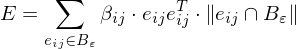
where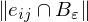 measures the length of the portion of the edge
measures the length of the portion of the edge 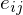 inside
inside 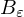 .
.
From this, we can compute:
The eigenvector to the largest eigenvalue of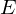 points into the direction of minimum curvature.
points into the direction of minimum curvature.
The direction of maximum curvature is orthogonal to that and can be found by taking the cross product with the normal vector.
We cannot derive the exact curvature values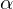 and
and 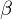 , but it is
, but it is
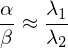
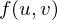 , we can take its taylor expansion
, we can take its taylor expansion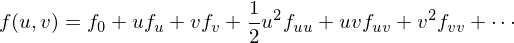
We can now reparametrize
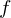 such that
such that 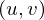 lies in the origin and the plane
lies in the origin and the plane 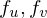 is parallel to
is parallel to 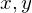
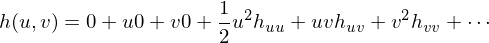
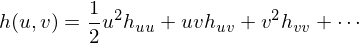
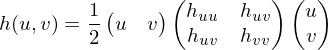
Since this matrix is symmetric and real-valued, we can do an eigendecomposition:
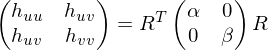
From the eigenvalues
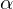 and
and 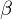 , we can derive two characteristics for local curvature:
, we can derive two characteristics for local curvature:Mean Curvature:
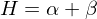
Gaussian Curvature:
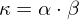
Which has the following interpretations:
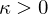 : Cap / Peak / Valley (elliptic)
: Cap / Peak / Valley (elliptic)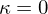 : Cylinder (parabolic)
: Cylinder (parabolic)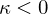 : Saddle (hyperbolic)
: Saddle (hyperbolic)The eigenvectors corresponding to
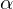 and
and 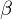 represent the respective curvature directions and are orthogonal.
represent the respective curvature directions and are orthogonal.Shape Operator
Approximates curvature for triangle meshes.
For each edge
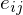 : atomic shape operator
: atomic shape operator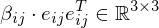
where
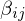 is the angle between the triangle normals
is the angle between the triangle normals 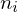
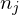 .
.Around a vertex, we compute the atomic shape operators of all edges in the vicinity
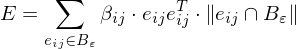
where
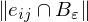 measures the length of the portion of the edge
measures the length of the portion of the edge 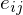 inside
inside 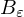 .
.From this, we can compute:
The eigenvector to the largest eigenvalue of
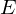 points into the direction of minimum curvature.
points into the direction of minimum curvature.The direction of maximum curvature is orthogonal to that and can be found by taking the cross product with the normal vector.
We cannot derive the exact curvature values
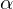 and
and 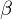 , but it is
, but it is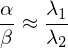
Flashcard info:
Author: janisborn
Main topic: Informatik
Topic: Computergrafik
School / Univ.: RWTH Aachen
City: Aachen
Published: 18.05.2022

