This flashcard is just one of a free flashcard set. See all flashcards!
57
Explain Photon Mapping!
Photon Generation
Shoot photons from all light sources:
Point light: Identical position. Uniform spherical distribution of directions.
Directional light: Identical direction. Uniform distribution of positions.
Area light: Uniform distribution of positions on the surface. Cos-thetha weighted distribution of directions.
For multiple light sources with different intensities: Adjust photon energy or photon frequency.
Optimization: Use projection maps to only shoot photons into directions where geometry is. Also requires scaling of energy:

Photon Tracing
On interaction with a surface with diffuse and specular reflection coefficients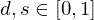 ,
, 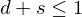 :
:
Russian Roulette: Generate random number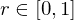
Information stored in the photon map: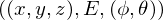
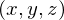 : position
: position
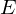 : photon power (flux per solid angle)
: photon power (flux per solid angle)
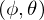 : angle of incidence
: angle of incidence
Radiance Estimate
Replace the recursive term in the Rendering Equation with a radiance estimate from the photon map. For a point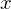 , find the
, find the 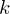 nearest neighbor samples from the photon map and compute
nearest neighbor samples from the photon map and compute
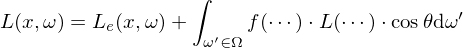
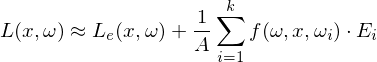
where
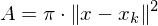
Rendering
Decompose the Rendering Equation
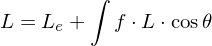
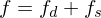
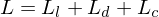
Evaluate the following factorizations:
Shoot photons from all light sources:
Point light: Identical position. Uniform spherical distribution of directions.
Directional light: Identical direction. Uniform distribution of positions.
Area light: Uniform distribution of positions on the surface. Cos-thetha weighted distribution of directions.
For multiple light sources with different intensities: Adjust photon energy or photon frequency.
Optimization: Use projection maps to only shoot photons into directions where geometry is. Also requires scaling of energy:

Photon Tracing
On interaction with a surface with diffuse and specular reflection coefficients
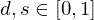 ,
, 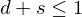 :
:Russian Roulette: Generate random number
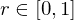
-
 : Diffuse reflection. Store in photon map. Continue tracing (TODO: Which direction?).
: Diffuse reflection. Store in photon map. Continue tracing (TODO: Which direction?). -
 : Specular reflection. Continue tracing (TODO: Which direction?).
: Specular reflection. Continue tracing (TODO: Which direction?). -
 : Absorption. Store in photon map.
: Absorption. Store in photon map.
Information stored in the photon map:
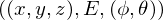
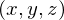 : position
: position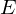 : photon power (flux per solid angle)
: photon power (flux per solid angle)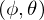 : angle of incidence
: angle of incidenceRadiance Estimate
Replace the recursive term in the Rendering Equation with a radiance estimate from the photon map. For a point
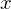 , find the
, find the 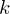 nearest neighbor samples from the photon map and compute
nearest neighbor samples from the photon map and compute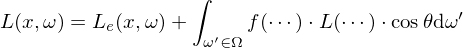
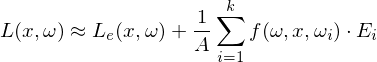
where
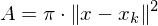
Rendering
Decompose the Rendering Equation
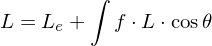
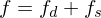
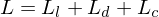
-
 : Diffuse reflections. Direction independent.
: Diffuse reflections. Direction independent. -
 : Specular reflections.
: Specular reflections. -
 : Direct illumination.
: Direct illumination. -
 : Diffuse illumination.
: Diffuse illumination. -
 : Caustic illumination.
: Caustic illumination.
Evaluate the following factorizations:
-
 Direct Illumination. Compute using ray casting / hemisphere sampling.
Direct Illumination. Compute using ray casting / hemisphere sampling. -
 Specular / Glossy Reflections. Compute using MCPT.
Specular / Glossy Reflections. Compute using MCPT. -
 Radiosity. Compute using radiance estimate from diffuse photon map.
Radiosity. Compute using radiance estimate from diffuse photon map. -
 Caustics. Compute using radiance estimate from caustic photon map.
Caustics. Compute using radiance estimate from caustic photon map.
Flashcard info:
Author: janisborn
Main topic: Informatik
Topic: Computergrafik
School / Univ.: RWTH Aachen
City: Aachen
Published: 18.05.2022

