This flashcard is just one of a free flashcard set. See all flashcards!
21
Give the smoothing operator for 3D meshes! Which weights can we use for this?
Smoothing Operator
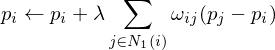
Uniform Weights
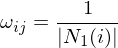
Move vertices into center of gravity of its 1-ring neighbors. Performs normal and tangential smoothing. Leads to a regular distribution of vertices.
Cotangent Weights
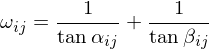
Denoting the area of the 1-ring around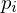 by
by 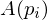 , cotangent weights move
, cotangent weights move 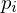 into the direction of
into the direction of 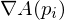 . Since in a planar configuration, moving
. Since in a planar configuration, moving 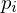 does not change
does not change 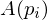 ,
, 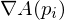 is normal to the mesh. Thus, cotangent weights have linear precision. Cotangent weights mostly do normal smoothing. They can become negative for very long triangles. However, if the mesh is Delaunay, Cotangent weights are positive.
is normal to the mesh. Thus, cotangent weights have linear precision. Cotangent weights mostly do normal smoothing. They can become negative for very long triangles. However, if the mesh is Delaunay, Cotangent weights are positive.
Mean Value Weights
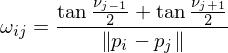
where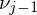 and
and 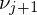 are the angles between the edge
are the angles between the edge 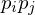 and the edges to the previous and next 1-ring neighbor, respectively. MVW have linear precision, they are always positive, but they are non-symmetric:
and the edges to the previous and next 1-ring neighbor, respectively. MVW have linear precision, they are always positive, but they are non-symmetric:
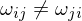 , in general
, in general
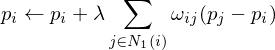
Uniform Weights
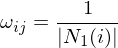
Move vertices into center of gravity of its 1-ring neighbors. Performs normal and tangential smoothing. Leads to a regular distribution of vertices.
Cotangent Weights
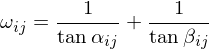
Denoting the area of the 1-ring around
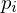 by
by 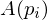 , cotangent weights move
, cotangent weights move 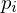 into the direction of
into the direction of 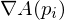 . Since in a planar configuration, moving
. Since in a planar configuration, moving 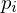 does not change
does not change 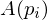 ,
, 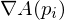 is normal to the mesh. Thus, cotangent weights have linear precision. Cotangent weights mostly do normal smoothing. They can become negative for very long triangles. However, if the mesh is Delaunay, Cotangent weights are positive.
is normal to the mesh. Thus, cotangent weights have linear precision. Cotangent weights mostly do normal smoothing. They can become negative for very long triangles. However, if the mesh is Delaunay, Cotangent weights are positive.Mean Value Weights
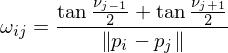
where
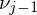 and
and 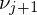 are the angles between the edge
are the angles between the edge 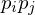 and the edges to the previous and next 1-ring neighbor, respectively. MVW have linear precision, they are always positive, but they are non-symmetric:
and the edges to the previous and next 1-ring neighbor, respectively. MVW have linear precision, they are always positive, but they are non-symmetric: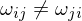 , in general
, in generalFlashcard info:
Author: janisborn
Main topic: Informatik
Topic: Computergrafik
School / Univ.: RWTH Aachen
City: Aachen
Published: 18.05.2022

