This flashcard is just one of a free flashcard set. See all flashcards!
97
Explain different ways to store meshes on disk and give the average amount of memory per vertex!
Face Set
For each triangle, store the position of all vertices.
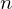 vertices
vertices
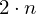 triangles
triangles
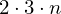 positions
positions
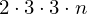 floats
floats
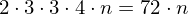 bytes
bytes
Shared Vertex
Store one list with positions of all vertices. For each triangle, store three indices into the vertex list.
For the vertex list:
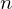 vertices
vertices
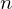 positions
positions
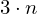 floats
floats
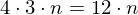 bytes
bytes
For the triangles:
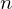 vertices
vertices
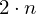 triangles
triangles
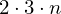 indices (i.e. ints)
indices (i.e. ints)
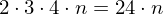 bytes
bytes
Total
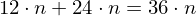 bytes
bytes
Triangle Strips
Store a list of vertex positions. Each triple of vertices in that list defines one triangle. (Note: triangles have alternating winding)
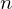 vertices
vertices
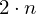 triangles
triangles
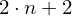 positions
positions
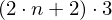 floats
floats
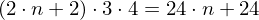 bytes
bytes
Representing general triangle meshes as triangle strips:
For each triangle, store the position of all vertices.
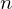 vertices
vertices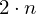 triangles
triangles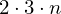 positions
positions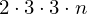 floats
floats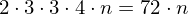 bytes
bytesShared Vertex
Store one list with positions of all vertices. For each triangle, store three indices into the vertex list.
For the vertex list:
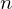 vertices
vertices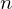 positions
positions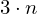 floats
floats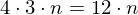 bytes
bytesFor the triangles:
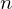 vertices
vertices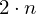 triangles
triangles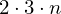 indices (i.e. ints)
indices (i.e. ints)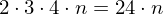 bytes
bytesTotal
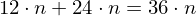 bytes
bytesTriangle Strips
Store a list of vertex positions. Each triple of vertices in that list defines one triangle. (Note: triangles have alternating winding)
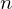 vertices
vertices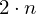 triangles
triangles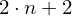 positions
positions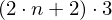 floats
floats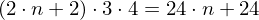 bytes
bytesRepresenting general triangle meshes as triangle strips:
- Apply 1:3-splits to allow for flexibility in mesh traversal.
- Generalized Triangle Strips: Store 1 additional bit per vertex, telling whether to replace the oldest or second-oldest vertex from the current triangle.
- Use multiple triangle strips for one mesh
Flashcard info:
Author: janisborn
Main topic: Informatik
Topic: Computergrafik
School / Univ.: RWTH Aachen
City: Aachen
Published: 18.05.2022

