elektrische Ladung
electric charge
positive charge:
- protons (atomic nucleus)
- (kat-) ions (ionized metal, ionized hydrogen, ionized gases... )
negative charge:
- electrons (atomic envelope)
- (an-) ions (remaining acid ions, ...)
force of repulsion between like charges
force of attraction between different charges
elementary charge, charge of an electron

positive charge:
- protons (atomic nucleus)
- (kat-) ions (ionized metal, ionized hydrogen, ionized gases... )
negative charge:
- electrons (atomic envelope)
- (an-) ions (remaining acid ions, ...)
force of repulsion between like charges
force of attraction between different charges
elementary charge, charge of an electron

Tags: Elektrik, Elektrizitätslehre, Ladung, Spannung, Strom
Source: www.dict.cc
Source: www.dict.cc
Tags: Bewegung, Dynamik, Kinematik, Mechanik
Source:
Source:
Tags: Bewegung, Dynamik, Kinematik, Mechanik
Source:
Source:
Kraft
force
directed quantity = vector
(draw an arrow with point of force + value + direction)
symbol:

Newton's law:
Hooke's law: (linear-elastic materials)
(linear-elastic materials)
gravity:

electrostatics:

directed quantity = vector
(draw an arrow with point of force + value + direction)
symbol:


Newton's law:

Hooke's law:
 (linear-elastic materials)
(linear-elastic materials)gravity:

electrostatics:

Tags: Elektrizitätslehre, Größen, Mechanik
Source:
Source:
Energie
energy
- a scalar physical quantity
- the ability to perform work, to take off heat or to emit light
symbol: E
unit: 1 Joule
symbol:

other units that also used:
electron volt: 1 eV = 1,602 * J
J
kilowatt hour: 1 kWh = 3,6 MJ
calorie :
1 cal = 4,2 J (small or gram calorie)
1 kcal = 1 Cal = 4,2 kJ (large / kilogram or food calorie)
- a scalar physical quantity
- the ability to perform work, to take off heat or to emit light
symbol: E
unit: 1 Joule
symbol:

other units that also used:
electron volt: 1 eV = 1,602 *
 J
Jkilowatt hour: 1 kWh = 3,6 MJ
calorie :
1 cal = 4,2 J (small or gram calorie)
1 kcal = 1 Cal = 4,2 kJ (large / kilogram or food calorie)
Tags: Elektrizitätslehre, Größen, Kernphysik, Mechanik, Thermodynamik
Source: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Energy
Source: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Energy
Energieformen
forms of energy
| potentielle Energie | potential energy |
| kinetische Energie | kinetical energy |
| elektrische Energie | electric energy, power |
| Wärmeenergie | heat / thermal / caloric energy |
| chemische Energie | chemical energy |
| Kernenergie | nuclear energy |
| Strahlungsenergie | radiant energy |
| zugeführte Energie | input energy |
| gespeicherte Energie | stored energy |
| Nutzenergie | useful energy |
| gebundene Energie | latent energy |
| Bindungsenergie | binding energy |
Tags: Elektrizitätslehre, Kernphysik, Mechanik, Thermodynamik
Source:
Source:
Leistung
power
the rate at which work is performed or energy is converted
Electric power: the rate at which electrical energy is transferred by a circuit
symbol: P
unit: 1 Watt
symbol:

formula:

the rate at which work is performed or energy is converted
Electric power: the rate at which electrical energy is transferred by a circuit
symbol: P
unit: 1 Watt
symbol:

formula:

Tags: Elektrik, Größen, Mechanik, Thermodynamik
Source:
Source:
Arbeit
work
mechanical work: the amount of energy transferred by a force
thermodynamics: the quantity of energy transferred from one system to another
symbol: W
unit: 1 Joule
symbol:
formula:

mechanical work: the amount of energy transferred by a force
thermodynamics: the quantity of energy transferred from one system to another
symbol: W
unit: 1 Joule
symbol:

formula:

Tags: Dynamik, Größen, Kinematik, Mechanik, Thermodynamik
Source: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Work
Source: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Work
Elektrizität
Electricity
Electric charge: a property of some subatomic particles, which determines their electromagnetic interactions. Electrically charged matter is influenced by, and produces, electromagnetic fields.
Electric current: a movement or flow of electrically charged particles, typically measured in amperes.
Electric field: an influence produced by an electric charge on other charges in its vicinity.
Electric potential: the capacity of an electric field to do work on an electric charge, typically measured in volts.
Electromagnetism: a fundamental interaction between the magnetic field and the presence and motion of an electric charge.
Electric charge: a property of some subatomic particles, which determines their electromagnetic interactions. Electrically charged matter is influenced by, and produces, electromagnetic fields.
Electric current: a movement or flow of electrically charged particles, typically measured in amperes.
Electric field: an influence produced by an electric charge on other charges in its vicinity.
Electric potential: the capacity of an electric field to do work on an electric charge, typically measured in volts.
Electromagnetism: a fundamental interaction between the magnetic field and the presence and motion of an electric charge.
Tags: Elektrik, Elektrizitätslehre, Ladung, Spannung, Strom
Source: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Electricity
Source: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Electricity
Geschwindigkeit
velocity (the rate of change of the position of one object)
speed (magnitude of velocity)
symbol: v
formula:

unit:

speed of light (the maximum speed in the universe)
symbol: c
value: c = 299 792 458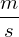
real animation: Speed_of_light_from_Earth_to_Moon
speed (magnitude of velocity)
symbol: v
formula:

unit:

speed of light (the maximum speed in the universe)
symbol: c
value: c = 299 792 458
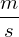
real animation: Speed_of_light_from_Earth_to_Moon
Tags: Dynamik, Kinematik, Licht, Mechanik, Optik
Source: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Light_speed
Source: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Light_speed
Lichtgeschwindigkeit
speed of light
light speed
symbol: c
Value in vacuum:
c = 299,792,458 metres per second = 1 Planck unit
(Sunlight takes about 8 minutes, 19 seconds to reach Earth, but, due to refraction, scattering, gravity and so on, about 100000 years to reach the surface of the sun from it's core)
- the maximum speed in the universe
- a constant of nature
- in a medium reduces the speed of light
- different types of light wave will travel at different speeds.
Approximate values:
300,000 kilometres per second
1,079 million kilometres per hour
186,000 miles per second
671 million miles per hour
173 astronomical units per day
real animation: Speed_of_light_from_Earth_to_Moon
light speed
symbol: c
Value in vacuum:
c = 299,792,458 metres per second = 1 Planck unit
(Sunlight takes about 8 minutes, 19 seconds to reach Earth, but, due to refraction, scattering, gravity and so on, about 100000 years to reach the surface of the sun from it's core)
- the maximum speed in the universe
- a constant of nature
- in a medium reduces the speed of light
- different types of light wave will travel at different speeds.
Approximate values:
300,000 kilometres per second
1,079 million kilometres per hour
186,000 miles per second
671 million miles per hour
173 astronomical units per day
real animation: Speed_of_light_from_Earth_to_Moon
Tags: Elektrik, Elektrizitätslehre, Licht, Optik, Relativitätstheorie
Source: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Light_speed
Source: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Light_speed
Ladungstrennung
Tags: Elektrik, Elektrizitätslehre, Ladung, Spannung
Source: www.dict.cc
Source: www.dict.cc
Tags: Elektrik, Elektrizitätslehre, Ladung, Spannung
Source:
Source:
Spannungsquelle
voltage source
DC:
cell
battery (3 or more cells in series connection)
accumulator = rechargeable battery or storage battery
AC:
alternating current generator (AC generator)
power supply unit
power transformer
power adaptor
DC:
cell
battery (3 or more cells in series connection)
accumulator = rechargeable battery or storage battery
AC:
alternating current generator (AC generator)
power supply unit
power transformer
power adaptor
Tags: Elektrik, Elektrizitätslehre, Strom, Stromkreis
Source: www.dict.cc, www.wikipedia.org
Source: www.dict.cc, www.wikipedia.org
Tags: Elektrik, Elektrizitätslehre, Stromkreis
Source: www.dict.cc
Source: www.dict.cc
Tags: Elektrik, Elektrizitätslehre, Strom, Stromkreis
Source: www.dict.cc
Source: www.dict.cc
Reihenschaltung
series circuit
series connection
I = constant
U = U1 + U2 + ...
R = R1 + R2 + ...
series connection
I = constant
U = U1 + U2 + ...
R = R1 + R2 + ...
Tags: Elektrik, Elektrizitätslehre, Strom, Stromkreis
Source: www.dict.cc
Source: www.dict.cc
Parallelschaltung
shunt circuit
parallel circuit
parallel connection
U = constant
I = I1 + I2 + ...

parallel circuit
parallel connection
U = constant
I = I1 + I2 + ...

Tags: Elektrik, Elektrizitätslehre, Spannung, Strom, Stromkreis
Source: www.dict.cc
Source: www.dict.cc
elektrischer Strom
electric current
a flow of electric charge (a phenomenon)
- in metals (electrons)
- in liquids (ions)
- in gases (electrons and ions)
- in vacuum (electrons or other charged particles)

a flow of electric charge (a phenomenon)
- in metals (electrons)
- in liquids (ions)
- in gases (electrons and ions)
- in vacuum (electrons or other charged particles)

Tags: Elektrik, Elektrizitätslehre, Größen, Strom
Source: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Electric_current
Source: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Electric_current
Tags: Elektrik, Elektrizitätslehre, Spannung, Strom, Stromkreis
Source: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Direct_current
Source: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Direct_current
Tags: Elektrik, Elektrizitätslehre, Spannung, Strom, Stromkreis
Source:
Source:
Tags: Elektrik, Elektrizitätslehre, Spannung, Strom, Stromkreis
Source: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Waveforms
Source: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Waveforms
Tags: Elektrik, Elektrizitätslehre, Spannung, Strom, Stromkreis
Source: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Line_voltage
Source: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Line_voltage
Stromstärke
current
(strength of electric current)
Def.: physival value - means the rate of flow of electric charge through the surface of the conductor (a quantity)
symbol: I
unit: ampère (the rate of one coulomb per second)
symbol: 1 A

(strength of electric current)
Def.: physival value - means the rate of flow of electric charge through the surface of the conductor (a quantity)
symbol: I
unit: ampère (the rate of one coulomb per second)
symbol: 1 A

Tags: Elektrik, Elektrizitätslehre, Größen, Strom
Source: www.dict.cc, www.wikipedia.org
Source: www.dict.cc, www.wikipedia.org
elektrische Spannung
voltage
(electrical potential)
Def: physical value (quantity) for galvanic separation
symbol: U
unit: volt
symbol: 1V

(see also: galvanic separation)
(electrical potential)
Def: physical value (quantity) for galvanic separation
symbol: U
unit: volt
symbol: 1V

(see also: galvanic separation)
Tags: Elektrik, Elektrizitätslehre, Größen, Strom
Source: www.dict.cc
Source: www.dict.cc
Strommesser
ammeter

- measuring instrument used to measure the electric current in a electric circuit
- always in series connection to the component
- is shown as a circle with the letter A (Ampére) inside

Tags: Elektrik, Elektrizitätslehre, Strom, Stromkreis
Source: www.dict.cc, www.wikipedia.org
Source: www.dict.cc, www.wikipedia.org
Spannungsmesser
voltmeter

- measuring instrument used for measuring the electrical potential difference between two points in an electric circuit
- in parallel connection to the component
- is shown as a circle with the letter V (Volt) inside

Tags: Elektrik, Elektrizitätslehre, Spannung, Strom, Stromkreis
Source: www.wikipedia.org
Source: www.wikipedia.org
(elektrischer) Widerstand
resistor (device)
resistance (value)
reluctance (magnetical resistance)
inductance (resistance of an inductor in alternating current = AC)
Def.: physical value, how strong the electric current is restricted
symbol: R
unit: 1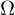 (Ohm)
(Ohm)
symbol and basic units:

formula:
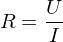
resistance (value)
reluctance (magnetical resistance)
inductance (resistance of an inductor in alternating current = AC)
Def.: physical value, how strong the electric current is restricted
symbol: R
unit: 1
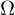 (Ohm)
(Ohm)symbol and basic units:

formula:
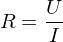
Tags: Elektrik, Elektrizitätslehre, Größen, Strom
Source: www.dict.cc
Source: www.dict.cc
Ionisation
ionisation
physical process of converting an atom or molecule into an ion by adding or removing charged particles such as electrons or other ions
physical process of converting an atom or molecule into an ion by adding or removing charged particles such as electrons or other ions
Tags:
Source: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ionization
Source: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ionization
spezifischer elektrischer Widerstand
resistivity
(specific electrical resistance or volume resistivity)
Def: measure of how strongly a material opposes the flow of electric current
symbol: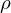 ("Rho")
("Rho")
unit:

or
(specific electrical resistance or volume resistivity)
Def: measure of how strongly a material opposes the flow of electric current
symbol:
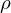 ("Rho")
("Rho")unit:

or

Tags: Elektrik, Elektrizitätslehre, Größen, Strom
Source: www.dict.cc
Source: www.dict.cc
Flashcard set info:
Author: schorai
Main topic: Physik
Topic: Bilingual D-En
City: Schwerin
Published: 06.11.2010
Tags: Sek I
Card tags:
All cards (35)
Bewegung (3)
Dynamik (4)
Elektrik (22)
Elektrizitätslehre (24)
Größen (9)
Kernphysik (2)
Kinematik (5)
Ladung (4)
Licht (2)
Mechanik (9)
Optik (2)
Spannung (10)
Strom (17)
Stromkreis (11)
Thermodynamik (4)















