Alkene polarity
Trans alkenes have higher melting points (symmetrical) and lower boiling points (less likely to be polar).
SP3 carbons donate electrons to SP2 carbons - orbitals more s character, closer to nucleus, more stable.

SP3 carbons donate electrons to SP2 carbons - orbitals more s character, closer to nucleus, more stable.

Tags: physical properties
Source:
Source:
Oxidation of a double bond
1. KMnO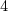
- mild conditions (vicinal diols)
- extreme conditions (carboxylic acids)
2. Ozonolysis
- mild conditions, reducing Zn/water environment (ketones/aldehydes)
- extreme conditions, oxidizing environment
3. NaBH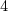 or LiAlH
or LiAlH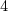
4. Peroxyacetic acids = CH CO
CO H or MCPBA (epoxide formation)
H or MCPBA (epoxide formation)
5. Hydroboration (NaBH , peroxide)
, peroxide)
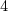
- mild conditions (vicinal diols)
- extreme conditions (carboxylic acids)
2. Ozonolysis
- mild conditions, reducing Zn/water environment (ketones/aldehydes)
- extreme conditions, oxidizing environment
3. NaBH
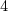 or LiAlH
or LiAlH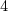
4. Peroxyacetic acids = CH
 CO
CO H or MCPBA (epoxide formation)
H or MCPBA (epoxide formation)5. Hydroboration (NaBH
 , peroxide)
, peroxide)Tags: rxns
Source:
Source:
Hammond Postulate
Related species that are similar in energy are also similar in structure. The structure of the transition state resembles the structure of the closest stable species.
-transition state for endothermic rxns resembles the product, exothermic the reactant.
-bromination transition state is closest to product. Thus reactivity very closely related to end-product stability (i.e. stability=speed).
-transition state for endothermic rxns resembles the product, exothermic the reactant.
-bromination transition state is closest to product. Thus reactivity very closely related to end-product stability (i.e. stability=speed).
Physical properties of alkanes
*chain length; increase
-bioling point
-melting point
-density
*branching; decrease
-boiling point
-density
*melting point and branching - determined by how symmetrical the molcule is; packing density. Easier to stack, more dense, higher melting point.
-bioling point
-melting point
-density
*branching; decrease
-boiling point
-density
*melting point and branching - determined by how symmetrical the molcule is; packing density. Easier to stack, more dense, higher melting point.
Tags: physical properties
Source:
Source:
Enantiomers
Non-superimposable mirror images.
Same physical properties except rotation of polarized light
Same chemical properties except with chiral molecules
Same physical properties except rotation of polarized light
Same chemical properties except with chiral molecules
Tags: Isomers
Source:
Source:
Tags: Isomers
Source:
Source:
Structural (Constitutional) Isomers
Same molecular weight and molecular formula.
Different atomic connectivity.
Different physical properties.
Different chemical properties.
*Number of isomers per CH formula.
Different atomic connectivity.
Different physical properties.
Different chemical properties.
*Number of isomers per CH formula.
Tags: Isomers
Source:
Source:
Stereoisomers
Same atomic connectivity, but different arrangement in space.
1. Conformational
2. Geometric
3. Enantiomers
4. Diastereomers
5. Meso compounds
1. Conformational
2. Geometric
3. Enantiomers
4. Diastereomers
5. Meso compounds
Tags: Isomers
Source:
Source:
Conformational Isomers (Conformers)
Do not need bond breaking to convert from one to another.
i.e. rotation about a bond.
Same physical and chemical properties.
i.e. rotation about a bond.
Same physical and chemical properties.
Tags: Isomers
Source:
Source:
Tags: Isomers
Source:
Source:
Geometric Isomers
Stereoisomerism at a double bond or cycloalkane.
i.e. cis or trans, (Z) or (E)
Different properties when difference in net polarities
i.e. cis or trans, (Z) or (E)
Different properties when difference in net polarities
Tags: Isomers
Source:
Source:




 hydrogen removal rather than
hydrogen removal rather than 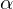 )
)

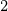 > ROH > H
> ROH > H

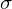 -MOs
-MOs



 hybrid orbitals
hybrid orbitals
 hybrid orbitals
hybrid orbitals
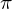 -MOs
-MOs


 in physical and chemical properties.
in physical and chemical properties.



