Function (Mapping)
A function (or mapping) 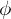 from a set
from a set 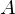 to a set
to a set 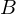 is a rule that assigns to each element
is a rule that assigns to each element  of
of 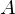 exactly one element
exactly one element 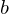 of
of 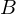 . The set
. The set 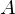 is called the domain of
is called the domain of 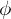 and
and 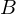 is called the range of
is called the range of 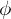 . If
. If 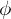 assigns
assigns 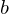 to
to  , then
, then 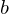 is called the image of
is called the image of  under
under 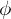 . The subset of
. The subset of 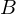 comprising all the images of elements of
comprising all the images of elements of 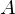 is called the image of A under
is called the image of A under 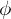 .
.
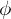 from a set
from a set 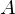 to a set
to a set 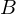 is a rule that assigns to each element
is a rule that assigns to each element  of
of 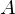 exactly one element
exactly one element 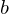 of
of 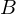 . The set
. The set 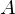 is called the domain of
is called the domain of 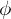 and
and 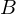 is called the range of
is called the range of 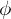 . If
. If 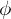 assigns
assigns 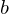 to
to  , then
, then 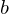 is called the image of
is called the image of  under
under 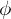 . The subset of
. The subset of 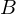 comprising all the images of elements of
comprising all the images of elements of 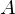 is called the image of A under
is called the image of A under 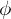 .
.Flashcard set info:
Author: Squiggleart
Main topic: Mathematics
Topic: Abstract Algebra
School / Univ.: West Chester University
Published: 25.05.2011
Tags: Algebra
Card tags:
All cards (10)
no tags



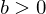 . Then
. Then 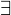 unique integers
unique integers 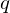 and
and 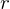 with the property that
with the property that 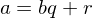 , where
, where  .
.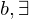 integers
integers  and
and 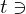 gcd(
gcd(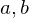 )
)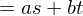 . Moreover, gcd(
. Moreover, gcd(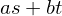 .
. be a set of integers containing
be a set of integers containing 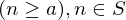 , then the integer
, then the integer 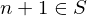 . Then,
. Then, 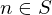 whenever every integer less than
whenever every integer less than 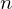 and greater than or equal to
and greater than or equal to 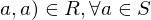 (reflexive)
(reflexive) implies
implies 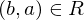 (symmetric)
(symmetric) and
and 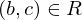 imply
imply  (transitive)
(transitive)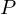 of
of 