What is market segmentation?
Dividing market into smaller groups with similar needs, characteristics or behaviours, that might require seperate marketing strategies or mixes
Most common Market segments are :
Geographic segmentation
Demographic segmentation
Psychographic segmentation
Behavioral segmentation
.
Most common Market segments are :
Geographic segmentation
Demographic segmentation
Psychographic segmentation
Behavioral segmentation
.
Targeting
The process of evaluating each market segment’s attractiveness and selecting one or more segments to enter.
Targeting broadly > - > - > - > >>>>> Targeting narrowly
Undifferentiated (mass)marketing > > Differentiated
(segmented)marketing > > Concentrated (niche) marketing > >
Micromarketing (local/individual) marketing
Targeting broadly > - > - > - > >>>>> Targeting narrowly
Undifferentiated (mass)marketing > > Differentiated
(segmented)marketing > > Concentrated (niche) marketing > >
Micromarketing (local/individual) marketing
Undifferentiated (mass) marketing
A market-coverage strategy in which a firm decides to ignore
market segment differences and go after the whole market with
one offer.
Differentiated (segmented) marketing
A market-coverage strategy in which a firm decides to target
several market segments and designs separate offers for
each.
Concentrated (niche) marketing
A market-coverage strategy in which a firm goes after a large
share of one or a few segments or niches.
share of one or a few segments or niches.
Micromarketing marketing
The practice of tailoring products and marketing programs to the needs and wants of specific individuals and local customer groups – includes local marketing and individual marketing.
Local marketing
Tailoring brands and promotions to the needs and wants of local customer groups – cities, neighbourhoods, and even specific stores.
Individual marketing
Tailoring products and marketing programs to the needs and preferences of individual customers – also labelled “markets-of-one marketing,” “customized marketing,” and “one-to-one marketing.”
Local marketing
Tailoring brands and promotions to the needs and wants of local customer groups – cities, neighbourhoods, and even specific stores.
Individual marketing
Tailoring products and marketing programs to the needs and preferences of individual customers – also labelled “markets-of-one marketing,” “customized marketing,” and “one-to-one marketing.”
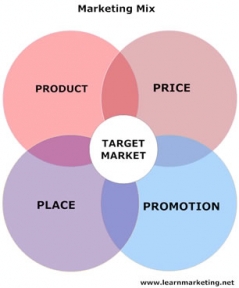
The 4 P’s
The major marketing mix tools are classified into four broad groups, called the four P’s of marketing:
Product – To deliver on its value proposition, the firm
must first create a need-satisfying market
offering.
Price – It must decide how much it will charge for the
offering and,
Place – how it will make the offering available to target
consumers.
Promotion – It must communicate with target
consumers about the offering and persuade them
on its merits.
Product – To deliver on its value proposition, the firm
must first create a need-satisfying market
offering.
Price – It must decide how much it will charge for the
offering and,
Place – how it will make the offering available to target
consumers.
Promotion – It must communicate with target
consumers about the offering and persuade them
on its merits.

Differentiation and Positioningon
Differentiation:
Actually differentiating the market offering to create superior customer value.
Positioning:
Arranging for a market offering to occupy a clear, distinctive, and desirable place relative to competing products in the minds of target customers.
3 steps for Differentiation + Positioning
1.Identifying a set of possible differentiation that create competitive advantage
2.Choosing advantages upon which to build a position
3.Selecting an overall positioning strategy.
Actually differentiating the market offering to create superior customer value.
Positioning:
Arranging for a market offering to occupy a clear, distinctive, and desirable place relative to competing products in the minds of target customers.
3 steps for Differentiation + Positioning
1.Identifying a set of possible differentiation that create competitive advantage
2.Choosing advantages upon which to build a position
3.Selecting an overall positioning strategy.
Types of channel intermediariesstion
Types of channel intermediaries
Upstream marketing channel partners
Set of firms that supply the raw materials, components, parts, information, finances, and expertise needed to create a product or service.
Downstream marketing channel partners
Channels that look forward toward the customer (Wholesalers and Retailers) and form a vital connection to the firm and its customers.
Upstream marketing channel partners
Set of firms that supply the raw materials, components, parts, information, finances, and expertise needed to create a product or service.
Downstream marketing channel partners
Channels that look forward toward the customer (Wholesalers and Retailers) and form a vital connection to the firm and its customers.
Product Life Cycle
The course of a product’s sales and profits over its lifetime.
Strategies:
Product development:
Finding + developing a new product idea, sales are zero.
Introduction:
Slow sales growth as product is introduced in the market.
Growth:
Rapid market acceptance and increasing profits.
Maturity:
Slowdown in sales growth because product has achieved.
Decline:
Sales fall off and profits drop.

Strategies:
Product development:
Finding + developing a new product idea, sales are zero.
Introduction:
Slow sales growth as product is introduced in the market.
Growth:
Rapid market acceptance and increasing profits.
Maturity:
Slowdown in sales growth because product has achieved.
Decline:
Sales fall off and profits drop.

Brand development
Line extensions
Extending an existing brand name to new forms, colours, sizes, ingredients, or flavours of an existing product category.
Brand extensions
Extending an existing brand name to new product categories.
Multiband
Companies often introduce additional brands in the same category.
New brands
When a company enters a new product category for which none of the company’s current brand names are appropriate.
Major Brand decisions

Brand’s positioning must be continuously communicated to consumers (advertising, personal experiences with the brand, word of mouth, company web pages)
Company needs to train its people to be customer centred (employees have to life the brand)
Company needs to periodically audit its brands strengths and weaknesses (SWOT)
STEP
Social, Technical, Economic, Political
Useful tool to understand risks associated with market
growth or decline, and as such the position, potential and
direction for a business.
Business measurement tool, looking at factors external of the
organization.
Useful tool to understand risks associated with market
growth or decline, and as such the position, potential and
direction for a business.
Business measurement tool, looking at factors external of the
organization.
Three levels of a product

Core product
“What is the buyer really buying?”
When designing products, marketers must first define the core, problem-solving benefits or services that consumers seek.
Actual product
Product planners need to develop product and service features, design, a quality level, a brand name, and packaging.
Augmented product
Company offers additional customer service and benefits around the product.
Classifying products
Consumer product
Product bought by final consumer for personal consumption.
Convenience product
Consumer product that customers usually buy frequently, immediately, and with a minimum of comparison and buying effort.
Shopping product
Consumer product that the customers, in the process of selection and purchase, characteristically compare on such bases as suitability, quality, price, and style.
Specialty product
Consumer product with unique characteristics or brand identification for which a significant group of buyers is willing to make a special purchase effort.
Unsought product
Consumer product that the consumer either does not know about or knows about but does not normally think of buying.
Industrial product
Product bought by individuals and organizations for further processing or for use in conducting a business.
Product bought by final consumer for personal consumption.
Convenience product
Consumer product that customers usually buy frequently, immediately, and with a minimum of comparison and buying effort.
Shopping product
Consumer product that the customers, in the process of selection and purchase, characteristically compare on such bases as suitability, quality, price, and style.
Specialty product
Consumer product with unique characteristics or brand identification for which a significant group of buyers is willing to make a special purchase effort.
Unsought product
Consumer product that the consumer either does not know about or knows about but does not normally think of buying.
Industrial product
Product bought by individuals and organizations for further processing or for use in conducting a business.
Company and Product costs
Cost based pricing
Setting prices based on the costs for producing, distributing, and selling the product plus a fair rate of return for its effort and risk.
Cost-plus pricing
Adding a standard markup to the cost of the product.
Break-even pricing (target profit pricing)
Setting price to break even on the costs of making and marketing a product; or setting price to make a target profit.
Setting prices based on the costs for producing, distributing, and selling the product plus a fair rate of return for its effort and risk.
Cost-plus pricing
Adding a standard markup to the cost of the product.
Break-even pricing (target profit pricing)
Setting price to break even on the costs of making and marketing a product; or setting price to make a target profit.
Channel levelsuestion
Channel level:
The number of intermediary levels indicates the length of a channel. Each layer of marketing intermediaries that performs some work in bringing the product and its ownership closer to the final layer is a channel level.
Direct marketing channel
A marketing channel that has no intermediary levels.
Indirect marketing channel
A channel containing one or more intermediary levels.
A greater number of levels means less control and greater channel complexity.
The number of intermediary levels indicates the length of a channel. Each layer of marketing intermediaries that performs some work in bringing the product and its ownership closer to the final layer is a channel level.
Direct marketing channel
A marketing channel that has no intermediary levels.
Indirect marketing channel
A channel containing one or more intermediary levels.
A greater number of levels means less control and greater channel complexity.
Geographic segmentation
World region or country - Noth America, Western Europe etc.
Country region- Pacific, Mountain, West North Central etc.
City or metro size- under 5.000; 5.000-20.000; etc.
Density- Urban, suburban, ex-urban, rural etc.
Country region- Pacific, Mountain, West North Central etc.
City or metro size- under 5.000; 5.000-20.000; etc.
Density- Urban, suburban, ex-urban, rural etc.
Demographic Segmentaion
Age
Gender
Family size- 1-2; 3-4, 5+
Family life cycle-young, single; (un)married with(out) children etc.
Income- under 20.000€, 20.000-30.000€, ..., 250.000 and over
Occupation- Professional and technical; manager, officals and proprietors; sales, crafspeople; supervisors; farmers; retired; students etc.
Education Grade shool.. high school graduate, college etc.
Religion
Race- Asian, Hispanic, Black, White
Generation- Baby boomer, Generation X, Millenials
Nationality
Gender
Family size- 1-2; 3-4, 5+
Family life cycle-young, single; (un)married with(out) children etc.
Income- under 20.000€, 20.000-30.000€, ..., 250.000 and over
Occupation- Professional and technical; manager, officals and proprietors; sales, crafspeople; supervisors; farmers; retired; students etc.
Education Grade shool.. high school graduate, college etc.
Religion
Race- Asian, Hispanic, Black, White
Generation- Baby boomer, Generation X, Millenials
Nationality
Psychographic segmentation
Social class- lower lowers, upper lowers, working class, middle class, upper middles, lower uppers, upper uppers
Lifestyle- achievers, strivers, survivors
Personality- compulsive, gregarious, authorican, ambitious
Lifestyle- achievers, strivers, survivors
Personality- compulsive, gregarious, authorican, ambitious
Behavioral segmentation
Occasions-regualar, special, hiliday, seasonal
Benefits- quality, service, economy, conveniance, speed etc.
User status -nonuser, exuser, potential user, first-time user etc.
User rates- light user, medium user, heavy user
Loyality status- none, medium, string, absolute
Readiness stage- (un)aware, informed, interested etc.
Attitude toward product enthuastic... indifferente.. etc.
Benefits- quality, service, economy, conveniance, speed etc.
User status -nonuser, exuser, potential user, first-time user etc.
User rates- light user, medium user, heavy user
Loyality status- none, medium, string, absolute
Readiness stage- (un)aware, informed, interested etc.
Attitude toward product enthuastic... indifferente.. etc.

Kartensatzinfo:
Autor: Elisa
Oberthema: Business Economics
Thema: Marketing
Schule / Uni: Hanze Hogeschool
Ort: Groningen
Veröffentlicht: 14.02.2010
Tags: Exam-relevant Keywords, Summary- Year 1, Marketing environment, customer-driven marketing strategy, product, pricing
Schlagwörter Karten:
Alle Karten (21)
keine Schlagwörter



