What's the primary problem with Cushings SYNDROME?
Glucocorticoid excess. (May or may not involve mineralcorticoid excess)
Exogenous (Most common)
Iatrogenic (given as medications)
Endogenous (Rare)
* ACTH Dependent -
-Pituitary = Cushing's Disease
-Ectopic source of ACTH
* ACTH-independent
Problem withe adrenals incorrectly producing too much Glucocorticoid
Exogenous (Most common)
Iatrogenic (given as medications)
Endogenous (Rare)
* ACTH Dependent -
-Pituitary = Cushing's Disease
-Ectopic source of ACTH
* ACTH-independent
Problem withe adrenals incorrectly producing too much Glucocorticoid
What are the Type II hypersensitivity AI diseases? What's the pathogenesis?
AI Hemolytic Anemia
IgG and IgM against RH antibodies on RBCs.
=> Complement activation & Enhanced phagocytosis
3 methods of destruction:
1) FcR+ on macrophages => Destruction
2) Binds comlement=> recruits Macrophages=>Destruction
3) Binds complement=> Complement mediated Lysis
Goodpasture's Sydnrome
IgG targets Type IV Collagen.
Antibody deposits => Kidney problems.
IgG and IgM against RH antibodies on RBCs.
=> Complement activation & Enhanced phagocytosis
3 methods of destruction:
1) FcR+ on macrophages => Destruction
2) Binds comlement=> recruits Macrophages=>Destruction
3) Binds complement=> Complement mediated Lysis
Goodpasture's Sydnrome
IgG targets Type IV Collagen.
Antibody deposits => Kidney problems.
What are the Thyroid AI diseases? What kind of Hypersensitivity?
Grave's Disease: Hyperthyroidism. Ab activates. Heat intolerance, nervousness, weight loss, BULGING EYES
Baby can get. Pregnant mother needs Plasmaphoresis to remove Ab.
Hashimoto's Disease: Hypothyroidism. Ab destroys. Germinal center generation => Goiter.
Middle Aged women common
Baby can get. Pregnant mother needs Plasmaphoresis to remove Ab.
Hashimoto's Disease: Hypothyroidism. Ab destroys. Germinal center generation => Goiter.
Middle Aged women common
What is SLE? When is it triggered? What's the main problem with SLE?
Intense inflammation
TIII hypersensitivity
Formation of immune responses in resonse to DNA, histones, ribosomes. This often happens after viral infection
Glomerulonephritis is a big problem because of kidney damage from the immune complexes
90% have arthritis.
Butterfly shaped skin rash
10:1 female to male
1:700 in women
1:250 among women of African or Asian descent.
TIII hypersensitivity
Formation of immune responses in resonse to DNA, histones, ribosomes. This often happens after viral infection
Glomerulonephritis is a big problem because of kidney damage from the immune complexes
90% have arthritis.
Butterfly shaped skin rash
10:1 female to male
1:700 in women
1:250 among women of African or Asian descent.
Rheumatoid Arthritis:
What are the effectors that mediate the disease? How frequent.? What is Rheumatoid Factor?
What are the effectors that mediate the disease? How frequent.? What is Rheumatoid Factor?
Effectors:
T cells, B cells, Macrophages & Neutrophils
Prostaglandins / Leukotrienes mediate inflammation
Lysosomal enzymes, proteinases, collagenases, TNF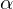 , IL-1, 8.
, IL-1, 8.
1-3% of the US.
80% have Anti-Antibodies called rheumatoid factor
Fc portion of human IgG
T cells, B cells, Macrophages & Neutrophils
Prostaglandins / Leukotrienes mediate inflammation
Lysosomal enzymes, proteinases, collagenases, TNF
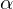 , IL-1, 8.
, IL-1, 8.1-3% of the US.
80% have Anti-Antibodies called rheumatoid factor
Fc portion of human IgG
MS
How common? What is the target & what kind of immune response causes it?
What are the main effector cells, and their effector molecules?
What are the 2 categories of MS?
How common? What is the target & what kind of immune response causes it?
What are the main effector cells, and their effector molecules?
What are the 2 categories of MS?
Main cause of neurological disability in young people
20-30 yo onset
Inflammation of CNS White Matter (myelinated)
Involves T-cell and macrophage => Axonal injury
CD4+ T cells secrete proinflammatory cytokines (TNF-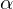 and IFN-
and IFN-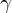 )
)
Relapse-remitting (RR) - cycle between acute attack and recover. Can accumulate damage
Progressive (PP) - getting worse
20-30 yo onset
Inflammation of CNS White Matter (myelinated)
Involves T-cell and macrophage => Axonal injury
CD4+ T cells secrete proinflammatory cytokines (TNF-
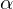 and IFN-
and IFN-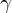 )
)Relapse-remitting (RR) - cycle between acute attack and recover. Can accumulate damage
Progressive (PP) - getting worse
ACTH-dependent vs. ACTH-Independent (if Endogenous)
| ACTH-dependent | ACTH-independent |
| Pituitary Dependent | Iatrogenic/ Factitious |
| Ectopic ACTH | Pigmented micronodular adrenal hyperplasia |
| Exogenous ACTH | Adrenal hyperplasia b/c of abnormal hormone receptor function |
* Macronodular adrenal hyperplasia can be both
Differential for ENDOgenous CS
ACTH Dependent:
2/3 are Cushings: 8:1 female/male. Gradual onset. 20-40 yo. Adenoma small / occult
1/6 Ectopic ACTH/CRH: 1:3 female/male. Oat cell carcinoma. Neuroendocrine tumors that might have somatostatin receptors
ACTH-Independent
1/6 are Adrenal (ACTH Independent): NO ANDROGEN EXCESS. Autoimmune / ectopic receptor / benign or malignant growth
2/3 are Cushings: 8:1 female/male. Gradual onset. 20-40 yo. Adenoma small / occult
1/6 Ectopic ACTH/CRH: 1:3 female/male. Oat cell carcinoma. Neuroendocrine tumors that might have somatostatin receptors
ACTH-Independent
1/6 are Adrenal (ACTH Independent): NO ANDROGEN EXCESS. Autoimmune / ectopic receptor / benign or malignant growth
Adrenal Meds
Metyrapone
Ketoconazole
Aminoglutethimide
Mitotane
Etomidate
Neuromodulatory agents
- 5HT antagonists [ Cyproheptadine, Rianserin ]
Dopamine antagonists [Bromocriptine]
Somatostatin Analogues [Octreotide]
GABA agonist - [Sodium Valproate]
Glucocorticoid Antagonist - [Mifepristone RU486]
Ketoconazole
Aminoglutethimide
Mitotane
Etomidate
Neuromodulatory agents
- 5HT antagonists [ Cyproheptadine, Rianserin ]
Dopamine antagonists [Bromocriptine]
Somatostatin Analogues [Octreotide]
GABA agonist - [Sodium Valproate]
Glucocorticoid Antagonist - [Mifepristone RU486]
What are the effects of Glucocorticoids by tissue?
| Metabolism | Liver, Fat, Muscle | Increased Glucose, Lipolysis, Muscle wasting |
| Calcium | Kidney, bone, GI | Reduced absorption, collagen synthesis |
| Immune | Cells | Inhibited |
| Skin | Antiproliferative | causes easy bruising |
| Breast | Epithelium | Galactorrhea |
| CV system / Kidney | Heart, Vasculature, Kidney | Increased ECF, Contractility, Response to Constrictors |
| Psychiatric | Mood, Sleep | Mood variable. Less REM, Increased Appetite |
What is 11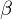 HSD-1 and 11HSD-2?
HSD-1 and 11HSD-2?
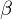 HSD-1 and 11HSD-2?
HSD-1 and 11HSD-2?11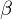 HSD-1 converts CORTISONE to CORTISOL, which can be used on a glucocorticoid receptor.
HSD-1 converts CORTISONE to CORTISOL, which can be used on a glucocorticoid receptor.
11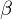 HSD-2 converts CORTISOL to CORTISONE, which doesn't interact with mineralcorticoid receptors (ie in the kidney)
HSD-2 converts CORTISOL to CORTISONE, which doesn't interact with mineralcorticoid receptors (ie in the kidney)
11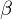 HSD2 is found in kidneys and other tissues with mineralcorticoid activity
HSD2 is found in kidneys and other tissues with mineralcorticoid activity
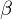 HSD-1 converts CORTISONE to CORTISOL, which can be used on a glucocorticoid receptor.
HSD-1 converts CORTISONE to CORTISOL, which can be used on a glucocorticoid receptor. 11
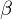 HSD-2 converts CORTISOL to CORTISONE, which doesn't interact with mineralcorticoid receptors (ie in the kidney)
HSD-2 converts CORTISOL to CORTISONE, which doesn't interact with mineralcorticoid receptors (ie in the kidney)11
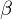 HSD2 is found in kidneys and other tissues with mineralcorticoid activity
HSD2 is found in kidneys and other tissues with mineralcorticoid activityWhat are the symptoms that Cushing's Shares with Metabolic Syndrome X? What are the things that are found in Cushings, but not Metabolic Syndrome X
| Shared | Cushing's Only |
| Abdominal Obesity | Osteoporosis |
| Insulin Resistance | Myopathy |
| Hypertension | Neuropyschiatric Syndromes |
| Glucose Intolerance | |
| PCOS/ hyperandrogenism | |
| Oligomenorrhea |
* Polycystic ovary disease
Flashcard set info:
Author: yaoyu
Main topic: Medicine
Topic: Endocrinology
Published: 10.02.2010
Card tags:
All cards (39)
no tags














